The Forex market may look chaotic at first glance — candlesticks moving every second, spreads changing, and currency pairs reacting immediately to global events. But behind this movement lies a clear, structured system. Understanding how the Forex market works is one of the most important steps for new traders. Without this foundation, even the best strategy cannot protect you from losses.
This guide breaks down everything in a simple, practical way: how prices move, who controls liquidity, how sessions influence volatility, what spreads mean, and why Forex behaves differently from stocks or crypto.
1. What Makes Forex Different From Other Financial Markets?
Forex is the world’s largest financial market, with $7.5 trillion in daily trading volume. But size alone doesn’t explain why the market behaves the way it does. Here are the structural differences that shape how Forex works:
1.1 No central exchange (OTC market)
Unlike stock markets such as NASDAQ or the Tokyo Stock Exchange, Forex is:
-
Decentralized
-
Borderless
-
Globally connected
-
Open 24 hours a day
All trading is executed electronically through a network of banks, brokers, financial institutions, and liquidity providers.
1.2 Forex prices are influenced by global forces
Currency prices are shaped by:
-
Interest rate decisions
-
Inflation data (CPI)
-
Employment reports (NFP)
-
Geopolitical events
-
Central bank speeches
-
Market sentiment
This is why major news events often cause sudden spikes, slippage, and spread widening.
1.3 Continuous market — no opening or closing price gaps (except Monday open)
Because Forex runs 24 hours, major gaps like those in stock markets rarely occur. The only significant gap usually appears at the Monday market open.
2. The Heart of Forex: Currency Pairs and Price Quotes
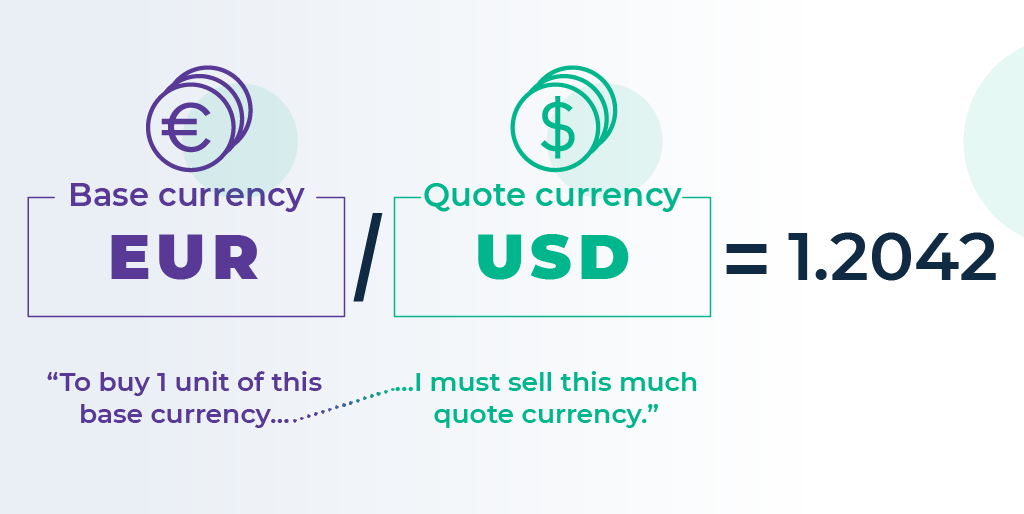
Example: EUR/USD = 1.0850
This means:
-
EUR = base currency
-
USD = quote currency
-
1 EUR = 1.0850 USD
2.1 Why Forex is always traded in pairs
Currencies don’t have standalone “prices” like stocks. Instead, their value is always measured relative to another currency.
You never simply “buy dollars”; you buy USD against another currency (like EUR/USD or USD/JPY).
2.2 Bid and Ask prices
Every pair has two prices:
-
Bid → price traders sell
-
Ask → price traders buy
Example:
EUR/USD → 1.0849 / 1.0851
Spread = 0.0002 = 2 pips
3. Who Moves the Forex Market? (Market Structure Explained)
Forex prices do not move randomly. They are shaped by a hierarchy of participants, each with different motivations and influence.
3.1 Tier 1: Central Banks
The “big bosses” of the Forex world:
-
Federal Reserve (FED)
-
European Central Bank (ECB)
-
Bank of Japan (BOJ)
-
Bank of England (BOE)
They influence currency prices through:
-
Interest rate changes
-
Quantitative easing
-
Bond purchase programs
-
Monetary policies
For example:
When the FED raises interest rates → USD strengthens.
3.2 Tier 2: Major Banks & Liquidity Providers
These institutions provide 90% of total market liquidity:
-
JPMorgan
-
Citibank
-
HSBC
-
Barclays
-
UBS
They quote bid/ask prices and execute massive orders for clients and hedge funds.
3.3 Tier 3: Hedge Funds & Investment Firms
They trade billions based on market trends, macroeconomic data, and algorithmic models.
3.4 Tier 4: Retail Brokers
Your broker connects retail traders to liquidity providers. They don’t set market prices — they display aggregated quotes from major banks.
3.5 Tier 5: Retail Traders (You)
Retail traders only account for 5–7% of daily volume. While small, they add liquidity and occupy a major share of short-term trading.
4. Forex Liquidity: Why It Matters for Every Trader
Liquidity refers to how easily you can buy or sell an asset at a stable price.
4.1 Why liquidity is important
High liquidity means:
-
Faster order execution
-
Lower spreads
-
Less slippage
-
More stable price movement
4.2 The most liquid pairs
-
EUR/USD
-
USD/JPY
-
GBP/USD
-
USD/CHF
-
AUD/USD
These pairs are perfect for beginners.
4.3 When does liquidity drop?
-
During Asian session
-
Before major economic news
-
On holidays
-
At Friday market close
-
At Monday market open
When liquidity is low, spreads widen and prices behave unpredictably.
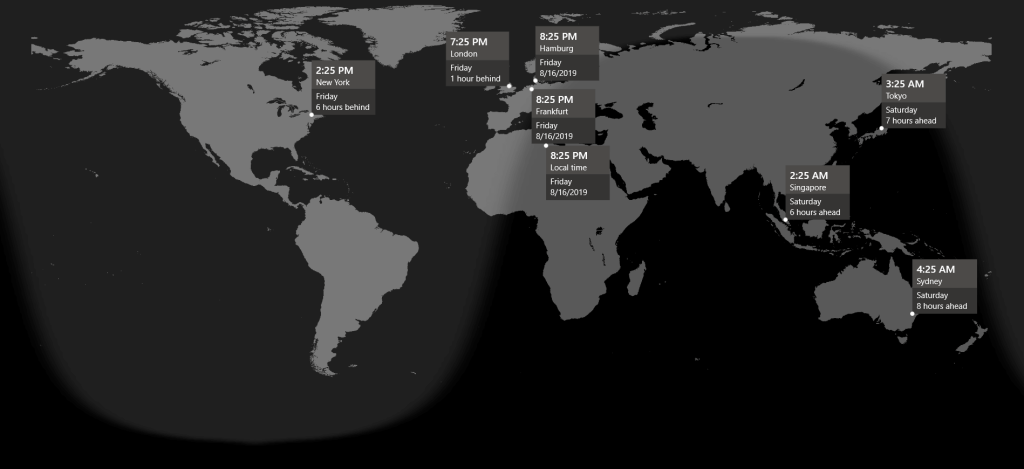
5. Forex Market Hours & Trading Sessions
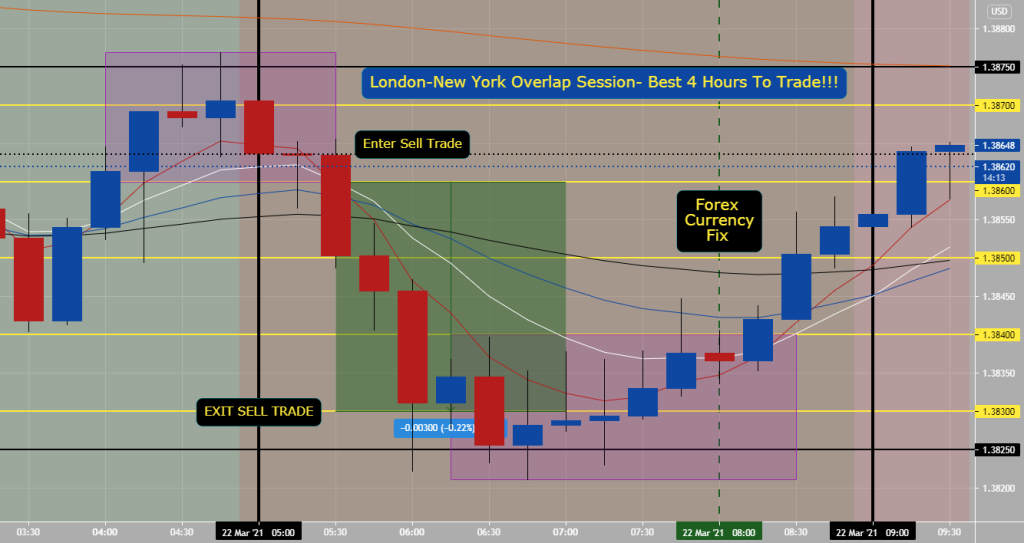
Forex operates 24/5 across four main sessions:
| Session | Time (GMT) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sydney | 22:00 – 07:00 | Slow, low volatility |
| Tokyo | 00:00 – 09:00 | Yen pairs active |
| London | 08:00 – 17:00 | High liquidity |
| New York | 13:00 – 22:00 | Strong volatility |
5.1 The most volatile time: London–New York overlap
⏰ 13:00 – 17:00 GMT
During this period:
-
Spreads drop
-
Volume increases
-
Strong trends form
-
Most day traders open positions
5.2 Asian session characteristics
-
Slow movement
-
Best for beginners to practice
-
Good for breaks and range trading strategies
6. Understanding Spread, Commission & Swap
6.1 Spread (the broker’s main fee)
Spread = Ask price – Bid price
Measured in pips.
Lower spread = cheaper trading.
Major pairs have spreads as low as 0.0–1.0 pip.
6.2 Commissions
Raw/ECN accounts charge:
-
$3–$7 per lot per side
Standard accounts:
Spread is slightly higher but no commission.
6.3 Swap (overnight fee)
If you hold trades overnight, you either:
-
Pay swap
-
Or receive swap (rare on major pairs)
Swap depends on interest rate differences between currencies.
Example:
If USD interest rates are higher than JPY → Buy USD/JPY may receive positive swap.
7. How Price Moves in the Forex Market (Mechanics Explained)
Forex prices move based on supply and demand — but the reasons behind that demand are more complex.
7.1 Fundamental factors
-
Interest rates
-
Economic announcements
-
Inflation data
-
Employment reports
-
GDP
-
Central bank speeches
-
Political events
7.2 Technical factors
-
Support/resistance zones
-
Trendlines
-
Liquidity pools
-
Order blocks
-
Chart patterns
7.3 Market sentiment
Sentiment reflects how traders feel about the market:
-
Risk-on → USD weak, JPY weak, equities up
-
Risk-off → USD strong, JPY strong, gold rises
7.4 Algorithmic and high-frequency trading
More than 70% of global Forex transactions are executed by automated algorithms.
They react instantly to:
-
Liquidity gaps
-
Price inefficiencies
-
News data
-
Volume clusters
This is why price often moves sharply seconds before major announcements.
8. How Brokers Execute Your Trades
Forex brokers use two main execution models:
8.1 A-Book (Straight Through Processing / ECN)
Your trades go directly to liquidity providers → no dealing desk.
Pros:
-
No conflict of interest
-
ECN spread
-
Faster execution
Cons:
-
Commission-based fees
8.2 B-Book (Market Maker)
The broker creates the opposite side of your trade.
Pros:
-
No commission
-
Lower capital requirement
Cons:
-
Potential conflict of interest
Most top-tier brokers use a hybrid model combining both.
9. How News Impacts Forex Prices
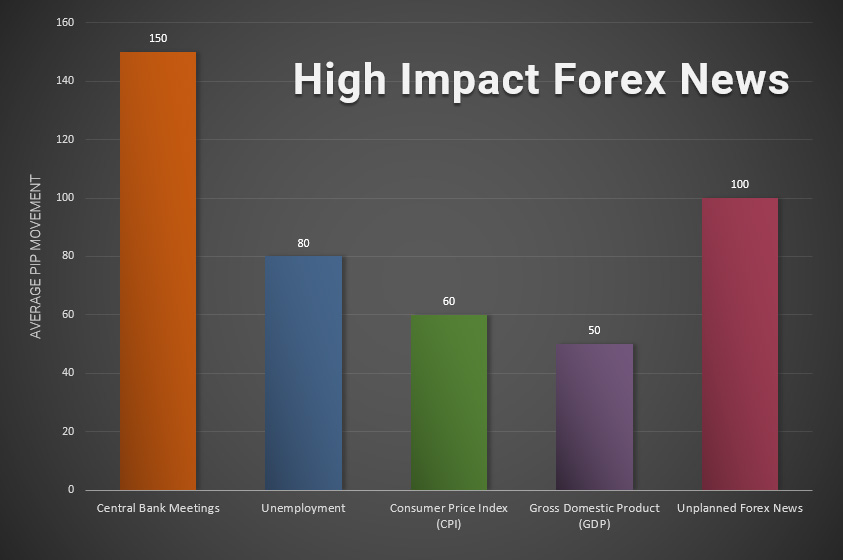
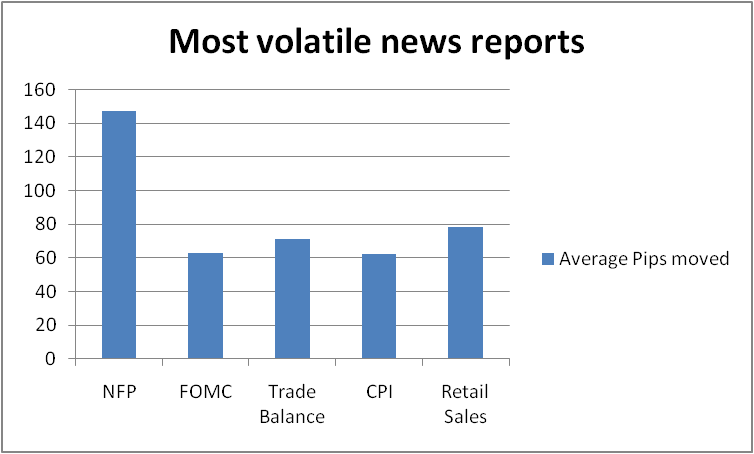
The Forex market reacts instantly to economic data. The most explosive news includes:
-
NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls)
-
CPI (Inflation data)
-
FOMC interest rate decision
-
GDP releases
-
Unemployment rates
During major news events:
-
Spreads widen (up to 10×)
-
Slippage increases
-
Market becomes unpredictable
-
Risk is significantly higher
Beginners should avoid trading during high-impact announcements.
10. Practical Tip: How to Use Market Structure to Trade Better
✔ Focus on the most liquid sessions
Avoid Asian session unless you trade ranges.
✔ Trade major pairs
They move smoothly and have low spreads.
✔ Always check the economic calendar
Never enter trades blindly during news.
✔ Understand where big orders sit
Liquidity pools often act as magnet zones for price.
11. Summary: Why Understanding Market Structure Makes You a Better Trader
Most beginners lose money not because of strategy, but because they don’t understand:
-
Why price moves
-
Why spreads widen
-
Why volatility changes every hour
-
Why stop-loss gets hit during news
-
Why sessions behave differently
When you understand how the Forex market works, everything becomes clearer:
-
Trends make sense
-
Fake breakouts become predictable
-
Volatility becomes manageable
-
Entries and exits become more accurate
Knowledge of market structure is the foundation of long-term success in Forex trading.